Classification of non-metallic inclusions
Task definition:
To determine the chemical composition of submicroscopic, non-metallic inclusions (NMI) in steel, analysis using a scanning electron microscope (SEM) with energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) is widely used (resolution limit approx. 200-300 nm)
However, since information about the chemical composition can also be derived from the backscattered electron (BSE) detector image of the SEM or the particle shape, it was investigated to what extent machine learning (ML) can be used for purely image-based classification without relying on complex EDX measurements
Realization:
- Data set: BSE images of the NMI, with associated ground truth is determined from the EDX spectrum
- Use of Deep Learning (DL): classification model based only on the BSE images
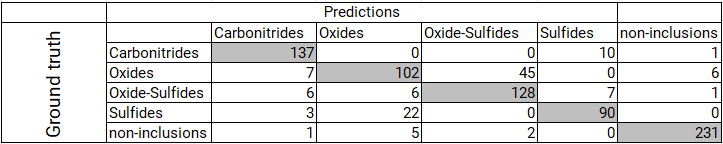
- In this application example, 5 classes are considered: Carbonitrides, oxides, sulphides, mixed oxide-sulphides as well as “non-inclusions” (e.g. pores, scratches, contaminations)
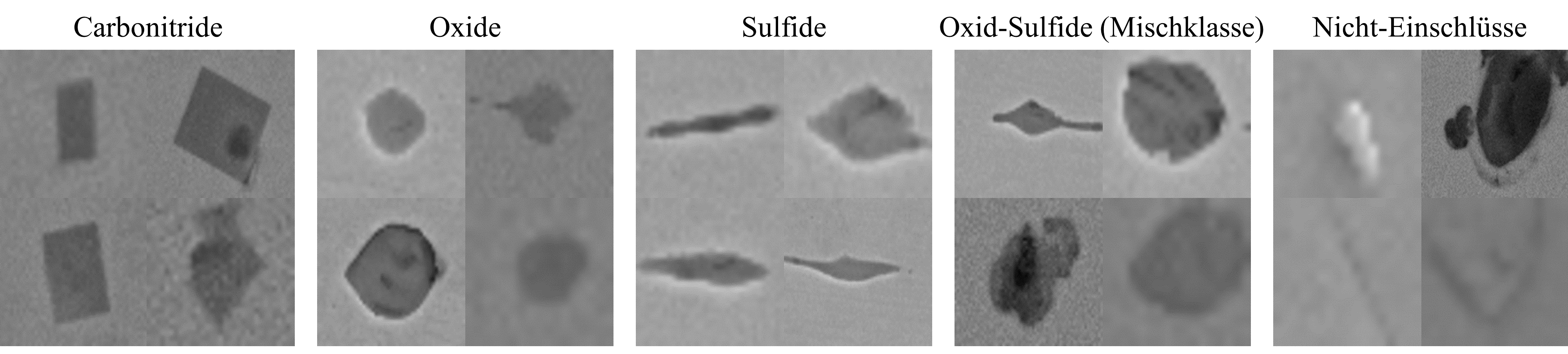

BSE recordings of the 5 classes
Results:
The DL model achieved an 84.9% accuracy in determining the chemical composition of the NMI using only the BSE image
Specifically, carbonitrides, sulphides and “non inclusions” can reliably be classified
Fields of application:
- Time saving by substituting EDX measurement with pure image evaluation
Partners for cooperation:
- Joint-stock company of Dillinger Huettenwerke, Dillingen/Saar
- Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh
Contact

Dr.-Ing. Dominik Britz
Deputy Head MECS Saarbrücken

Adrian Thome, M.Sc.
Chief Operating Officer

