Antimicrobial surfaces
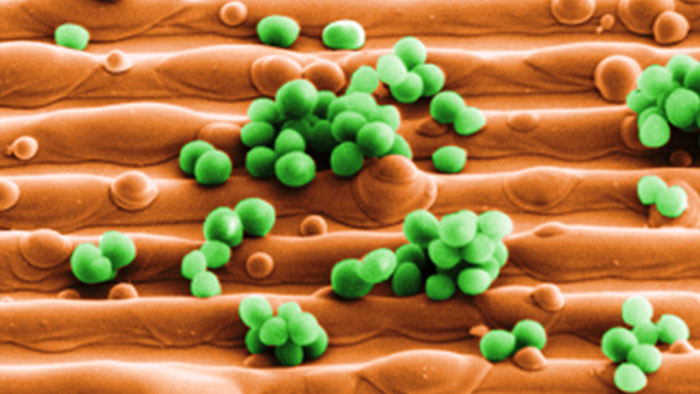
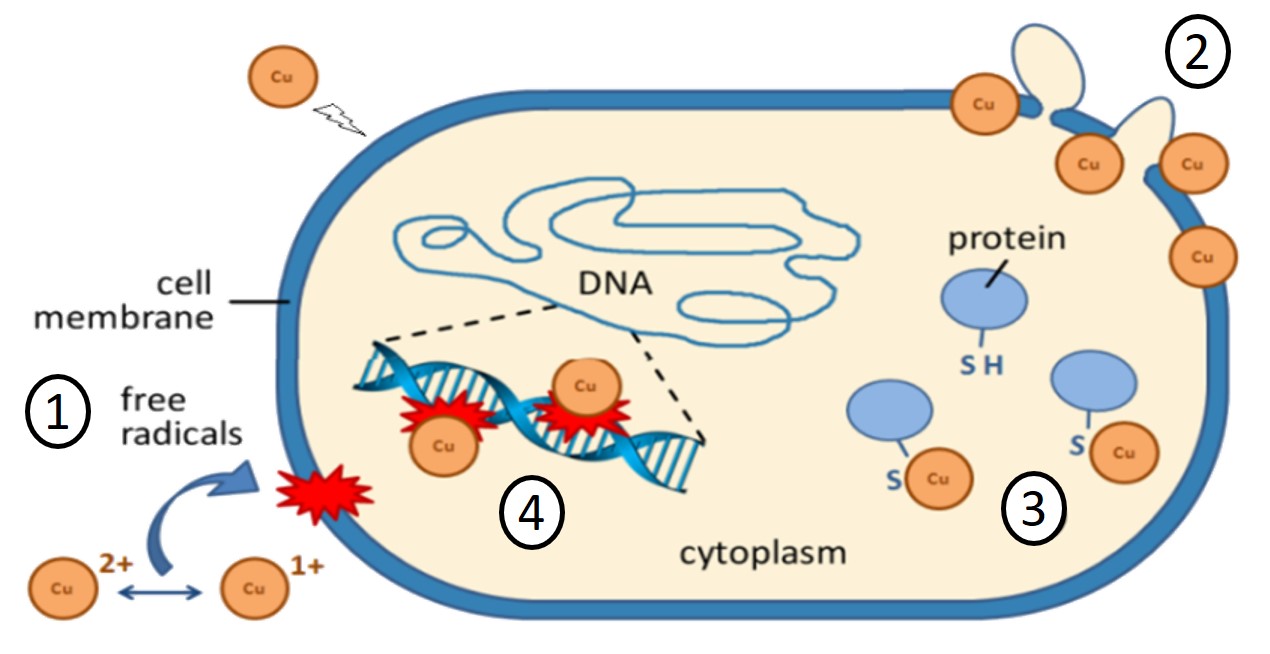
- Attack and destruction of the cell membrane by free copper ions (1/2)
- Deactivation of selected proteins (3)
- Decomposition of DNA (4)
For active killing, direct contact of the bacteria with the copper surfaces plays a decisive role. Copper ions alone are not sufficient for effective antimicrobial action.
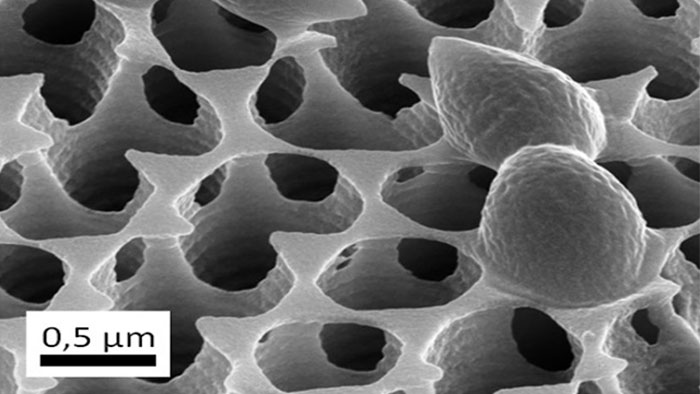
Surfaces have long been known to carry pathogens and have posed major problems, especially for hospitals, not only since COVID-19. By structuring a surface using Direct Laser Interference Patterning (DLIP), we can specifically determine one dominant of two antimicrobial mechanisms and investigate the interactions at our site:
- Structures smaller than bacteria reduce the contact areas and thus have an anti-adhesive effect
- Structures the size of bacteria increase the contact areas, thereby enhancing the antimicrobial effect of copper
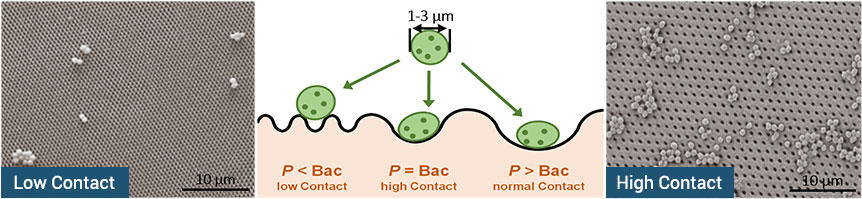
According to Helbig 2016
Contact for questions

Dr.-Ing Dominik Britz
Deputy Head MECS Saarbrücken

Adrian Thome, M. Sc
Project Leader
Further areas of application
Machine Learning (ML)
Our services range from feasibility studies with our various approaches to exploratory data analysis with unsupervised ML.
Triboelectrical characterization
Complementary to our microstructure analysis, we are able to perform a wide variety of triboelectric measurements (e.g. electrical resistivity and coefficient of friction during mating tests) under controlled conditions.
Failure analysis
In the area of failure analysis, in addition to identifying and analyzing causes of fracture, we are also able to fully characterize components on both the macro and micro scales.
Correlative Microscopy
A correlative characterization of microstructures serves as a benchmark for automated microstructure recognition and as a starting point for machine learning approaches.




